2 Plots In One Figure Matlab
| MATLAB Function Reference |
Browse other questions tagged matlab plot legend matlab-figure or ask your own question. The Overflow Blog The Loop: Our Community & Public Platform strategy & roadmap for Q1 2021.
- I have my own function called 'histogramwithmeansigmalines'. The output of the function is a figure. So I use this function to generate two figures (which is a histogram). I want the two figures to be in one figure like two subplot (2,1,1 & 2,1,2).
- I have my own function called 'histogramwithmeansigmalines'. The output of the function is a figure. So I use this function to generate two figures (which is a histogram). I want the two figures to be in one figure like two subplot (2,1,1 & 2,1,2).
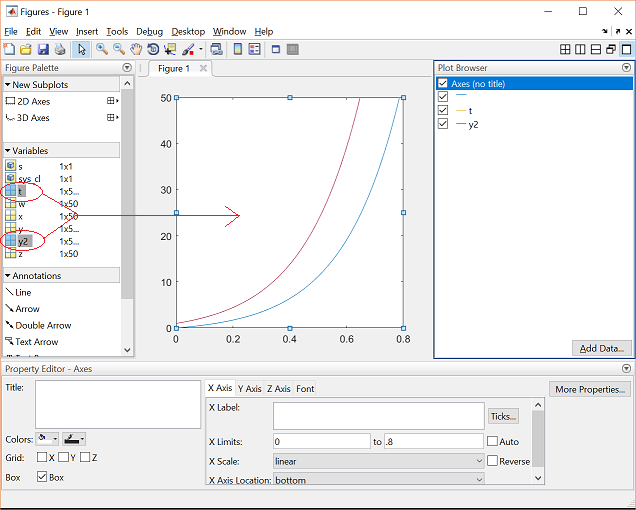
Create axes object in tiled positions
Syntax
Description
subplot divides the current figure into rectangular panes that are numbered rowwise. Each pane contains an axes object. Subsequent plots are output to the current pane.
h = subplot(m,n,p), or subplot(mnp) breaks the Figure window into an m-by-n matrix of small axes, selects the pth axes object for for the current plot, and returns the axis handle. The axes are counted along the top row of the Figure window, then the second row, etc. For example,
plots income on the top half of the window and outgo on the bottom half. If the CurrentAxes is nested in a uipanel, the panel is used as the parent for the subplot instead of the current figure. The new axes object becomes the current axes.
If p is a vector, it specifies an axes object having a position that covers all the subplot positions listed in p.
subplot(m,n,p,'replace')If the specified axes object already exists, delete it and create a new axes.
subplot(m,n,p,'align')positions the individual axes so that the plot boxes align, but does not prevent the labels and ticks from overlapping.
subplot(h)makes the axes object with handle h current for subsequent plotting commands.
subplot('Position',[left bottom width height])creates an axes at the position specified by a four-element vector. left, bottom, width, and height are in normalized coordinates in the range from 0.0 to 1.0.
h = subplot(...)returns the handle to the new axes object.
Remarks
If a subplot specification causes a new axes object to overlap any existing axes, then subplot deletes the existing axes object and uicontrol objects. However, if the subplot specification exactly matches the position of an existing axes object, then the matching axes object is not deleted and it becomes the current axes.
subplot(1,1,1) or clf deletes all axes objects and returns to the default subplot(1,1,1) configuration.

You can omit the parentheses and specify subplot as
where m refers to the row, n refers to the column, and p specifies the pane.
Special Case - subplot(111)
The command subplot(111) is not identical in behavior to subplot(1,1,1) and exists only for compatibility with previous releases. This syntax does not immediately create an axes object, but instead sets up the figure so that the next graphics command executes a clf reset (deleting all figure children) and creates a new axes object in the default position. This syntax does not return a handle, so it is an error to specify a return argument. (This behavior is implemented by setting the figure's NextPlot property to replace.)
Examples
To plot income in the top half of a figure and outgo in the bottom half,
The following illustration shows four subplot regions and indicates the command used to create each.
The following combinations produce asymmetrical arrangements of subplots.
You can also use the colon operator to specify multiple locations if they are in sequence.
See Also
axes, cla, clf, figure, gca
Basic Plots and Graphs for more information

| sub2ind | subsasgn |
© 1994-2005 The MathWorks, Inc.
This example shows how to combine plots in the same axes using the hold function, and how to create multiple axes in a figure using the tiledlayout function. The tiledlayout function is available starting in R2019b. If you are using an earlier release, use the subplot function instead.
Combine Plots in Same Axes
By default, new plots clear existing plots and reset axes properties, such as the title. However, you can use the hold on command to combine multiple plots in the same axes. For example, plot two lines and a scatter plot. Then reset the hold state to off.
When the hold state is on, new plots do not clear existing plots or reset axes properties, such as the title or axis labels. The plots cycle through colors and line styles based on the ColorOrder and LineStyleOrder properties of the axes. The axes limits and tick values might adjust to accommodate new data.
Display Multiple Axes in a Figure
You can display multiple axes in a single figure by using the tiledlayout function. This function creates a tiled chart layout containing an invisible grid of tiles over the entire figure. Each tile can contain an axes for displaying a plot. After creating a layout, call the nexttile function to place an axes object into the layout. Then call a plotting function to plot into the axes. For example, create two plots in a 2-by-1 layout. Add a title to each plot.
Note: This code uses the tiledlayout function, which is available starting in R2019b. If you are using an earlier release, use the subplot function instead.
Create Plot Spanning Multiple Rows or Columns
To create a plot that spans multiple rows or columns, specify the span argument when you call nexttile. For example, create a 2-by-2 layout. Plot into the first two tiles. Then create a plot that spans one row and two columns.
Modify Axes Appearance
Modify the axes appearance by setting properties on each of the axes objects. You can get the axes object by calling the nexttile function with an output argument. You also can specify the axes object as the first input argument to a graphics function to ensure that the function targets the correct axes.
For example, create two plots and assign the axes objects to the variables ax1 and ax2. Change the axes font size and x-axis color for the first plot. Add grid lines to the second plot.
Control Spacing Around the Tiles
You can control the spacing around the tiles in a layout by specifying the Padding and TileSpacing properties. For example, display four plots in a 2-by-2 layout.
Minimize the spacing around the perimeter of the layout and around each tile by setting the Padding and TileSpacing properties to 'none'.
Display Shared Title and Axis Labels
You can display a shared title and shared axis labels in a layout. Create a 2-by-1 layout t. Then display a line plot and a stem plot. Synchronize the x-axis limits by calling the linkaxes function.
2 Plots In One Figure Matlab Function
Add a shared title and shared axis labels by passing t to the title, xlabel, and ylabel functions. Move the plots closer together by removing the x-axis tick labels from the top plot and setting the TileSpacing property of t to 'compact'.
See Also
Functions
2 Plots In One Figure Matlab Functions
holdnexttiletiledlayouttitle